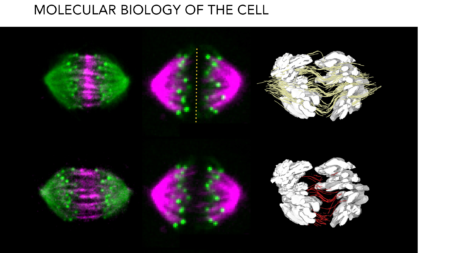
In partnership with the Center for Membrane and Cell Physiology, Redemann Lab is looking to uncover and understand the underlying principles of spindle assembly on a nano-scale level.
Mitotic spindles are highly dynamic, microtubule based constructions that function to segregate the chromosomes during cell division. The dynamic properties of microtubules in spindles are modulated by many factors, including polymerases, depolymerases, motor proteins, cross-linkers and other microtubule associated proteins, of which many are conserved throughout eukaryotic organisms. Despite this evolutionary conservation of essential factors, there is a remarkable variability in spindle organization and mechanics between organisms and tissues within species.
The Redemann Lab is interested in uncovering and understanding the underlying principles of spindle assembly on a nano-scale level. In particular we are focussing of the mechanisms and mechanical principles of chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis and how errors in these phenomena lead to cancer and infertility
We are using a combination of large scale 3D reconstruction of spindles by electron tomography and state-of-the-art light microscopy as well as CRISPR technology in our lab. Ultimately we are using the dynamic and ultra structural data to develop and test models of spindle formation and mechanics.