Diabetes Impact
Impact of Prediabetes and Diabetes in Virginia
- 1 million Virginians have prediabetes (1/3 of the state population!)
- 9 of 10 Virginians don’t know they have prediabetes
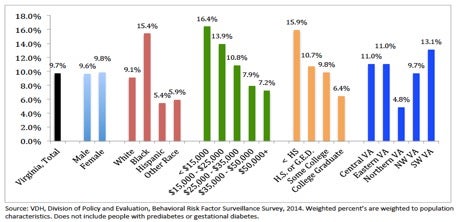
- ~632,000 Virginians have diabetes (9.6% of the population)
- 1 out of 4 persons in Virginia do not know they have diabetes
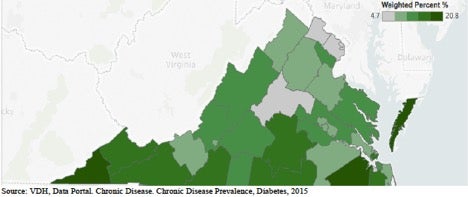
- Diabetes is most prevalent in rural areas of the state and where the poverty rates are the highest:
- Eastern Shore Health District (Eastern Shore peninsula)
- 20.8 %
- Lenowisco Health District (Appalachian counties of Southwest Virginia)
- 19.1% in Lee, Scott, Wise Counties and Norton City
- Western Tidewater Health District (South Eastern Virginia)
- 18 % in Isle of Wight and Franklin Counties and Southampton and Suffolk Cities
- Nearly one quarter of the 65+ population are living with diabetes in Virginia. Prevalence of diabetes increases dramatically with every 10-year age group
- Eastern Shore Health District (Eastern Shore peninsula)
Impact of Diabetes Prevention and Diabetes Self-Management Education Programs
Prevention of Diabetes
- Lifestyle management is an integral component of prevention and treatment of diabetes.
- People with prediabetes can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by changing their lifestyle. Diabetes prevention programs (DPP) are available throughout Virginia (Figure 4) to educate and support people with prediabetes so that they can prevent or at least delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
- DPP programs are effective. Participants in community programs reduced the incidence of diabetes by 41% through healthier eating patterns, regular physical activity and moderate weight loss. They also experienced reductions in blood glucose, blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Medicare will cover DPPs starting April 2018. Many employers and insurances cover DPP programs as well.
Prevention of Complications of Diabetes
Most of the complications of diabetes can be prevented through good blood glucose control in the early stages of diabetes. If complications have already occurred, further harm can be prevented through:
- Glucose control – Improved control of blood glucose can reduce the risk of microvascular complications in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. These complications include those involving the eyes, kidneys and nervous system.
- Blood pressure control –Reduction in high blood pressure decreases the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease as well as the microvascular complications. Monitoring and medical management of high blood pressure is important.
- Control of blood cholesterol – Control of LDL and HDL cholesterol and triglycerides can reduce the cardiovascular complications of diabetes significantly. Improved diet and use of medications will help control blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Care of feet – The care of feet is very important since persons with diabetes are often diagnosed with neuropathy and unable to sense pain from cuts or injuries to their feet. Not feeling a foot injury may lead to an infection if not treated in time. Daily foot checks are recommended.
- Kidney Protection – Monitoring blood pressure and taking blood pressure medications as prescribed, quit smoking, and limiting salt intake may reduce the risk of kidney damage.
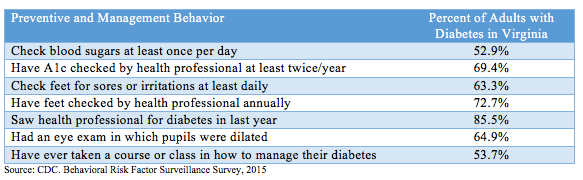
Figure 3. Percent of Adults with Diabetes in Virginia who Engage in Preventive and Self-Management Diabetes Practices in 2015
Diabetes Self-Management Education
- More than 45% of Virginians with diabetes have never taken a class on how to better manage their diabetes.
- 6% of people who have less than a high school education have never taken a class as compared to 36.7% of people with more than a high school education.
- Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) is a standard component of diabetes care. People with diabetes are educated and support is provided around seven self-care behaviors: healthy eating, being active, monitoring, taking medication, problem solving, healthy coping and reducing risks.
- Engaging adults with type 2 diabetes in DSMES results in improvements in A1C by as much as 1%.
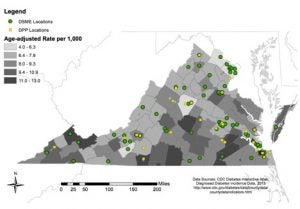
Figure 4. Diabetes Self-Management & Education (DSME) and Diabetes Prevention Programs in Virginia as of 2017