Media Archive
Josh Colston, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, studies the complex health challenges faced by children and families in low-resource areas and tropical regions.
 Jinyi Tang, PhD, a research scientist in the Sun Lab, part of the Beirne B. Carter Center for Immunology Research and the Department of Medicine’s Division of Infectious, received a K99/R00 transition award from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Jinyi Tang, PhD, a research scientist in the Sun Lab, part of the Beirne B. Carter Center for Immunology Research and the Department of Medicine’s Division of Infectious, received a K99/R00 transition award from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
 To combat the potentially life-threatening infection C. difficile, UVA researchers William A. Petri, MD, PhD, Jr., and Girija Ramakrishan, PhD, in the Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health, are studying fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) to provide novel therapeutic approaches to C. difficile colitis prevention and management.
To combat the potentially life-threatening infection C. difficile, UVA researchers William A. Petri, MD, PhD, Jr., and Girija Ramakrishan, PhD, in the Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health, are studying fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) to provide novel therapeutic approaches to C. difficile colitis prevention and management.
 Eczema Treatment Cuts Risk of Death From COVID-19
Eczema Treatment Cuts Risk of Death From COVID-19
A monoclonal antibody used to treat asthma and eczema can improve survival for patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, a clinical trial at UVA Health suggests.
 Powerful Computer Models ID Weaknesses in Deadly C. difficile
Powerful Computer Models ID Weaknesses in Deadly C. difficile
The researchers say their new work represents a significant step forward in the use of a form of predictive computer modeling called GENREs to battle infectious diseases.
 Innovator of the Year Made Herculean Efforts Throughout the Pandemic
Innovator of the Year Made Herculean Efforts Throughout the Pandemic
At the beginning of the pandemic, when federal health agencies couldn’t provide enough COVID-19 tests, Mathers worked with Melinda Poulter to help create in-house tests to meet the demand at UVA and at hospitals across the state.
“When lenacapavir is used for
treatment in people living with HIV,
it has to be given in combination
with other drugs. If a person
stops taking treatment, the virus
will return. Lenacapavir is also
not a vaccine. If a person using
lenacapavir for PrEP stops getting
doses, they can be at risk for
acquiring HIV.” Jackson said
READ MORE
 Bird flu cases are on the rise
Bird flu cases are on the rise
with a possible human-to-human
transmitted case, and confirmed
first case in a child in California,
increasing the concerns of a wider
outbreak.
However, infectious disease expert
Dr. Patrick Jackson with UVA Health
said while the disease is evolving
and becoming more transmissible,
it is not time panic.
WATCH VIDEO
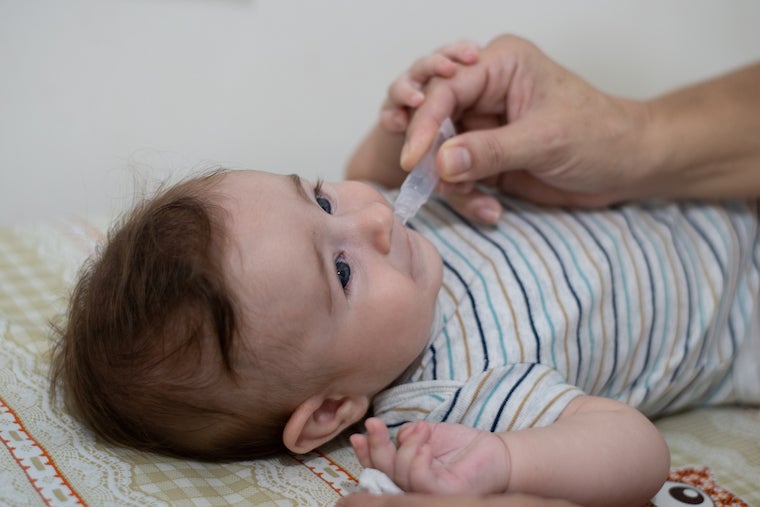

Baby taking droplet vaccine to prevent rotavirus.
University of Virginia researchers are developing a flexible online tool for navigating information used in the fight to save children from deadly diarrheal diseases by identifying transmission hotspots and accelerating the deployment of treatments and new vaccines.
 “What I really love is the translational work we’re doing and knowing the ability of our work can directly impact to the public health.”
“What I really love is the translational work we’re doing and knowing the ability of our work can directly impact to the public health.”
 “Our work impacts human health for Virginians and for communities globally, such as those with whom we deeply collaborate in Tanzania, Uganda, and Bangladesh.
“Our work impacts human health for Virginians and for communities globally, such as those with whom we deeply collaborate in Tanzania, Uganda, and Bangladesh.
 To better understand E. coli and its impact on human health, UVA Today reached out to Melissa Kendall, PhD, an associate professor in the Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Cancer Biology, and William Petri, MD, PhD, the Wade Hampton Frost Professor of Medicine, to get their insights into the outbreak.
To better understand E. coli and its impact on human health, UVA Today reached out to Melissa Kendall, PhD, an associate professor in the Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Cancer Biology, and William Petri, MD, PhD, the Wade Hampton Frost Professor of Medicine, to get their insights into the outbreak.
“Our work impacts human health for Virginians and for communities globally, such as those with whom we deeply collaborate in Tanzania, Uganda, and Bangladesh.

Patrick Jackson, MD
Program Director
University of Virginia School of Medicine scientists have uncovered a key reason why HIV remains so difficult to cure: Their research
shows that small changes in the virus affect how quickly or slowly it replicates, and how easily or stubbornly it can reawaken from
hiding.
These insights bring researchers closer to finding ways to flush out the dormant virus and eliminate it for good.
“HIV treatment is lifesaving but also lifelong,” said Patrick Jackson, MD, one of the two lead authors on the paper. “Understanding how the virus stays latent in cells could help us develop a lasting cure for HIV.”
 The University of Virginia magazine talks with Dr. Edward Egelman, Dr. William Petri, Dr. William Knaus, Dr. Mariano Garcia-Blanco, and Dr. Audrey Brown about the impact of federal research funding uncertainty.
The University of Virginia magazine talks with Dr. Edward Egelman, Dr. William Petri, Dr. William Knaus, Dr. Mariano Garcia-Blanco, and Dr. Audrey Brown about the impact of federal research funding uncertainty.
“There are breakthroughs that happen literally every week in biomedical research in the U.S.,”
said William Petri (Grad ’80, Med ’82), vice chair for research at the Department of Medicine. “It’s one of the things where we lead the world.”
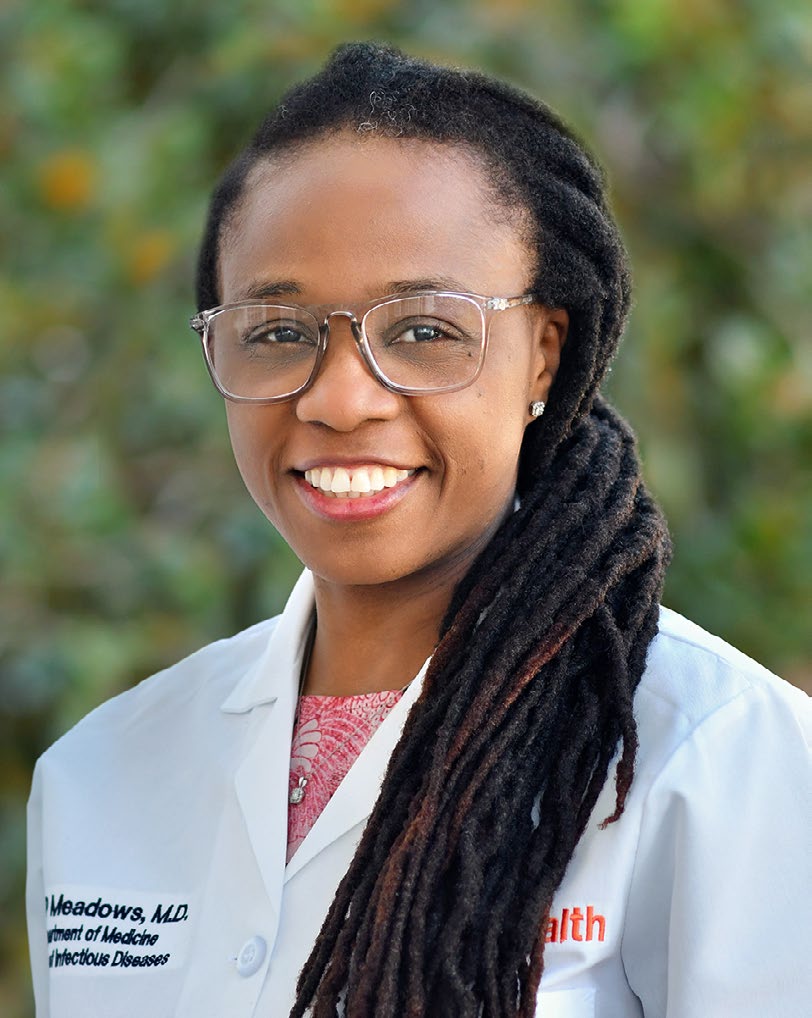 Idu Meadows, MD, a 2nd-year Infectious Diseases fellow, collaborated with researchers at Kibong’oto Infectious Diseases Hospital in Tanzania’s Kilimanjaro to investigate disability following tuberculosis treatment. More than 9
Idu Meadows, MD, a 2nd-year Infectious Diseases fellow, collaborated with researchers at Kibong’oto Infectious Diseases Hospital in Tanzania’s Kilimanjaro to investigate disability following tuberculosis treatment. More than 9
million people survive tuberculosis every year, but the majority suffer some form of disability. Dr. Meadows and her collaborators found among adults with respiratory symptoms after TB cure, a TB-survivor-led therapy program improved walking distance, the first of its kind.
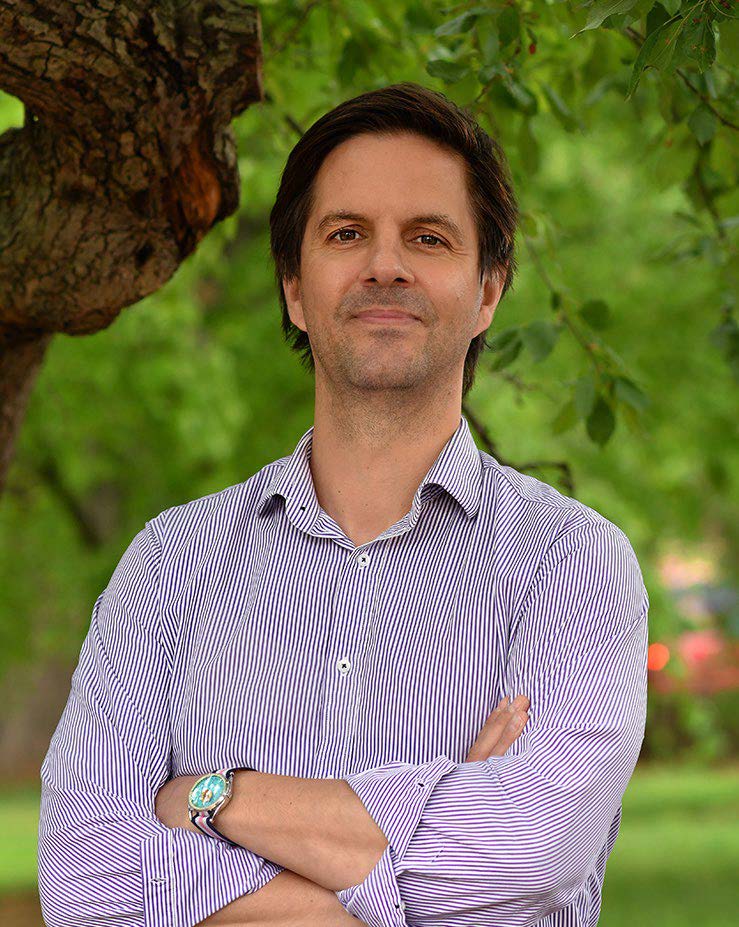 Dr. Josh Colston’s research into housing quality and disease prevention is featured in the
Dr. Josh Colston’s research into housing quality and disease prevention is featured in the
University of Virginia magazine. By identifying risk factors for disease clusters, public health
professionals can better pinpoint the potential presence of a disease. “You can then target it for some kind of intervention,” said Dr. Colston.
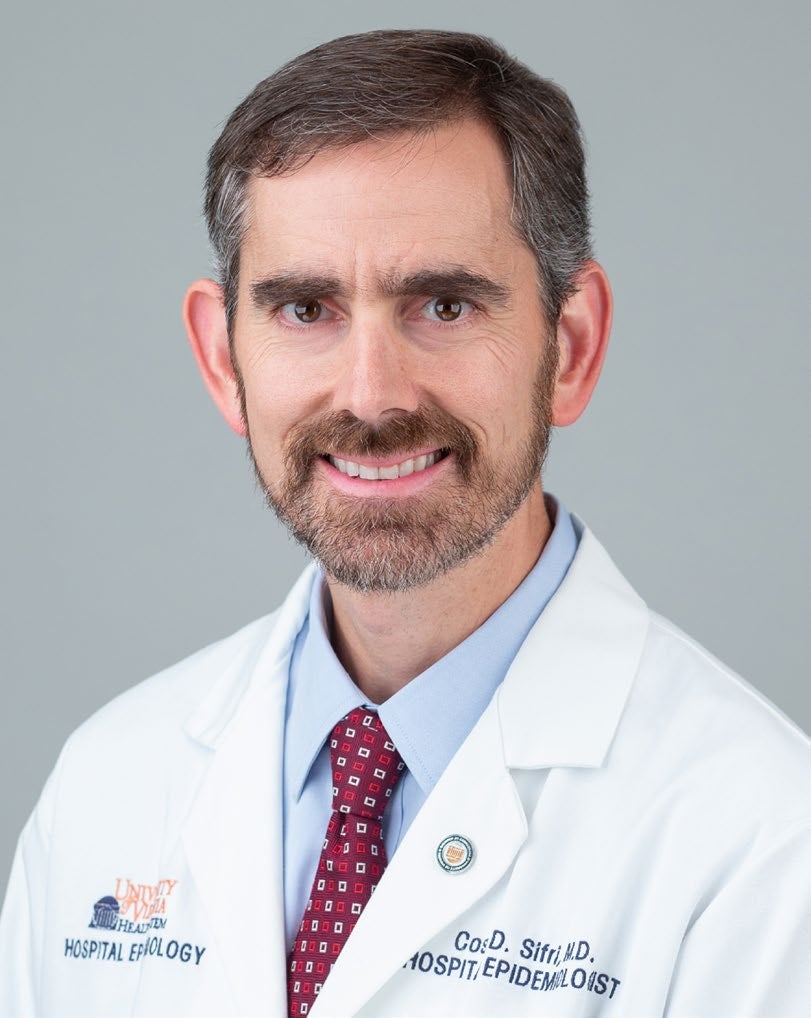 Dr. Costi Sifri talks with Richmond NPR affiliate VPM about measles. Two doses of the measles, mumps and rubella vaccine provide lifetime protection, but unvaccinated people
Dr. Costi Sifri talks with Richmond NPR affiliate VPM about measles. Two doses of the measles, mumps and rubella vaccine provide lifetime protection, but unvaccinated people
— and infants who are too young to be vaccinated — are very susceptible to infection. “Unfortunately, these circumstances are certainly a pressure test on some preparedness
planning, and we’re rolling out and developing more resources for our frontline clinicians to be able to respond to this so we do have a
measles control plan,” said Dr. Sifri.
 Grant GianGrasso graduated from the University in Virginia, for the second time, in 2024. As an undergraduate at UVA, GianGrasso conducted research in the lab of Chelsea Marie Braun, an
Grant GianGrasso graduated from the University in Virginia, for the second time, in 2024. As an undergraduate at UVA, GianGrasso conducted research in the lab of Chelsea Marie Braun, an
associate professor of medicine, who focuses on infectious diseases.
There he studied cryptosporidium, a diarrheal parasite affecting children, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
Doctors at the University of Virginia Medical Center wanted to test patients who may be infected by the novel coronavirus. First, they had to overcome obstacles that set them back weeks.
The lab directors at the University of Virginia Medical Center felt powerless.
In early March, people began arriving with symptoms of COVID-19. One complained of a cough and had just returned from Wuhan, the Chinese city where the outbreak erupted. An elderly patient, already on end-of-life care, had a mysterious respiratory infection. Another, struggling to breathe, had come from a nursing home.
Each needed a test for the coronavirus. The hospital had none to offer.
“Testing is so critical,” said Amy Mathers, an infectious disease physician at the hospital and associate director of its clinical laboratory. “Everybody was just hounding me, and I could see how not having in-house testing was getting worse and worse and worse for the patients and the staff.”

